AI Legal Assistant — Agentic AI in Legal Contract Management
Every morning, Sarah, the general counsel at a mid-sized tech company, arrives at her desk to find dozens of contracts needing review. Like most legal professionals, she spends her days juggling urgent requests, managing bottlenecks, and trying to keep pace with growing business demands. But Sarah’s world is changing, thanks to a new type of artificial intelligence that works alongside her team.
How to Leverage Agentic AI in Legal Workflows?
This technology—known as Agentic AI—represents a fundamental shift in how computers help legal professionals. Unlike traditional AI tools that passively wait for commands, Agentic AI systems act as autonomous “agents” that independently perform complex tasks with minimal supervision. These digital collaborators don’t just respond to specific questions; they expect needs, make decisions, and execute multi-step workflows on their own initiative.
Imagine watching over Sarah’s shoulder as she receives a new vendor agreement. Instead of immediately diving into a detailed review, she forwards it to her AI Agent.
Sarah’s AI Legal Assistant completes these time-consuming tasks within minutes:
- It scans the entire agreement against company standards, highlighting deviations
- It flags that the liability cap falls 50% below acceptable thresholds
- It suggests specific replacement language drawn from approved templates
- It routes the document to Sarah’s procurement specialist with concerns clearly marked
- It sets calendar reminders for upcoming negotiation deadlines
- It automatically logs the interaction in the matter management system

This isn’t science fiction—it’s the practical reality of Agentic AI today. The system doesn’t simply process information; it completes entire workflows by chaining together multiple capabilities: language understanding, decision-making, document creation, and process management. The key distinction lies in its autonomy and initiative—qualities that make it a true partner rather than merely a tool.
The Practical Importance of Agentic AI in Legal Workflows
The numbers tell a compelling story. At Sarah’s company, three attorneys manage about 2,500 contracts yearly. Each agreement typically requires 3-4 hours of careful review—totaling between 7,500-10,000 hours of contract work each year. This mathematics creates an impossible equation: the legal team simply cannot review every document thoroughly while maintaining reasonable response times.
This scenario plays out in legal departments across industries, creating ripple effects throughout organizations. Sales cycles lengthen as contracts sit in review queues. Business units develop workarounds to bypass legal bottlenecks, often accepting unfavorable terms. Attorneys work evenings and weekends, leading to burnout and turnover. And despite these efforts, inconsistencies creep in as tired reviewers miss subtle issues that later become expensive problems.
How Does the AI Legal Assistant Solve the Bottleneck Problem?
Agentic AI addresses these challenges directly. When Sarah’s team put their system into practice, they saw review times go down by 70% for standard agreements. The technology ensures consistent application of company standards across thousands of documents, preventing costly oversights that often slip through during rushed human reviews. Perhaps most important, faster contract cycles accelerate revenue recognition—directly affecting the company’s financial performance.
If you’re facing similar challenges, start by mapping your contract landscape. Count how many agreements your team processes monthly, track the average time required for each document type, and identify which contracts consume disproportionate resources. These baseline measurements will help you measure potential efficiency gains and build the business case for implementing Agentic AI in your organization.
Automated Contract Drafting
For Michael, a sales executive at Sarah’s company, the old process of obtaining a new customer agreement meant emailing to legal and waiting—sometimes for days—while a priority deal hung in the balance. Now, he accesses the company’s AI contract agent through a simple dashboard. He answers five quick questions about his healthcare client in California, including specific deal structure, compliance requirements, and desired terms.
Within two minutes—not days—the system produces a complete 15-page agreement incorporating healthcare privacy provisions, California-specific clauses, and the company’s latest approved language. The document arrives ready for client review, with the most likely negotiation points already highlighted for Michael’s attention.
This capability doesn’t materialize overnight. To implement similar automated drafting in your organization, start by identifying your highest-volume contract types—typically NDAs, sales agreements, and vendor contracts. These repetitive documents offer the quickest wins. Next, build a comprehensive template library with approved alternative clauses for different scenarios. Develop clear business rules defining when specific provisions should be included or excluded based on factors like industry, geography, or transaction value. Finally, launch a pilot with a single contract type, letting you refine the process before expanding to more complex agreements.
Intelligent Review and Risk Analysis
The true power of Agentic AI emerges during contract review, where it identifies potential issues before they become problems. When Sarah’s team receives a complex vendor agreement, their AI agent conducts a comprehensive analysis that catches issues even experienced attorneys might miss during a time-pressured review.
In a recent case, the system flagged three critical risks: a confidentiality provision missing standard exclusions for independently developed information, payment terms contradicting milestone dates in the statement of work, and a limitation of liability clause capped at just six months of fees—well below company standards. The agent didn’t just identify these problems; it suggested specific replacement language, calculated the financial risk exposure ($250,000 based on contract value), and routed the highest-risk items directly to the proper legal specialist for targeted review.
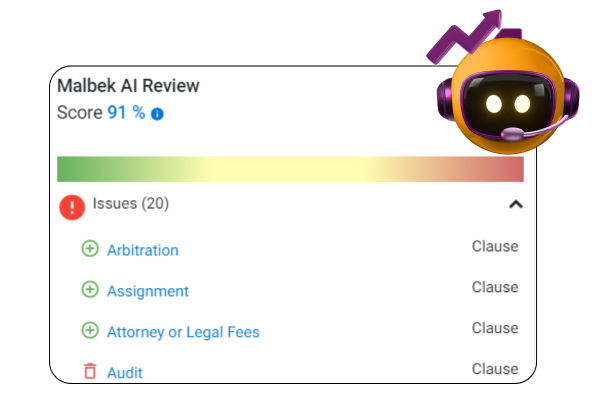
This capability dramatically improves risk management while reducing attorney workload. To implement similar intelligent review functions, define your organization’s risk tolerance thresholds across different contract types and create a comprehensive playbook documenting unacceptable, negotiable, and preferred terms. Develop a clause library with alternative language for common negotiation points, and begin with a pilot program focusing on high-volume, lower-risk agreements like NDAs or standard vendor contracts before tackling more complex documents.
AI-powered Workflow Automation
Perhaps the most immediate impact of Agentic AI comes from eliminating the manual handoffs and administrative tasks that typically slow contract review. In Sarah’s legal department, contracts no longer sit idle while waiting for attention. The AI agent keeps documents moving through the review process without constant human intervention.
When a sales representative recently uploaded a client’s redlined master services agreement, the system immediately analyzed the document, identifying 12 changed clauses. It automatically approved seven changes falling within pre-approved parameters while routing three pricing changes to finance, sending two high-risk liability changes to legal with specific concerns highlighted, setting deadline reminders based on the client’s requested close date, and telling the sales representative of the expected completion timeline.
This automated triage reduced the legal department’s review burden by 60% while ensuring oversight for risky provisions. The sales team received faster responses, and attorneys focused their limited time on substantive issues rather than routine approvals.
How to Start Your Workflow Automation?
Implementing workflow automation begins with mapping your current contract review process, identifying all stakeholders and approval steps. Create clear delegation rules defining which changes require which approvals and establish service level agreements for different review types and priority levels. Configure notification preferences and escalation paths for delayed reviews to prevent bottlenecks.
Obligation Management using Agentic AI
The value of Agentic AI extends well beyond the signature date. Some of the most significant benefits emerge after contracts are executed, as the system turns static documents into active management tools that track commitments and deadlines.
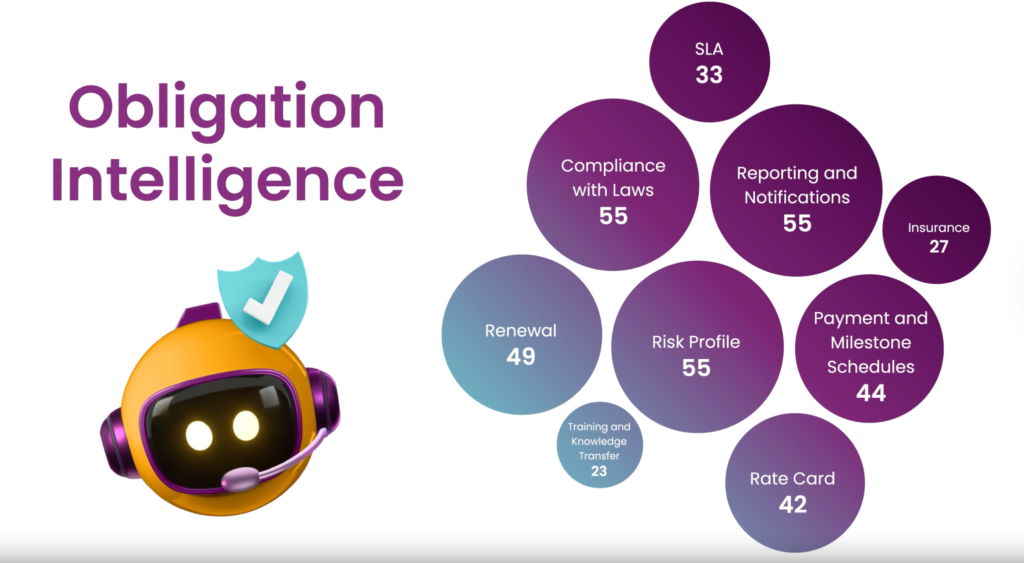
After Sarah’s team closed a complex services agreement last quarter, their AI agent extracted 27 obligations, eight key dates, and four conditional requirements from the document. It created calendar alerts for the renewal notice period (90 days before end), quarterly performance reviews, and minimum purchase requirements. Each department received customized duty summaries relevant to their responsibilities, and the system established a tracking protocol that sends escalating reminders as deadlines approach.
Never Miss a Deadline Again
This proactive management prevents common issues like missed renewal windows, overlooked price increase caps, or forgotten reporting requirements—problems that previously cost the company hundreds of thousands in unnecessary expenses and lost opportunities.
To implement effective duty management, start by identifying which contractual commitments often create compliance challenges in your organization. Establish clear ownership for different duty categories, create standardized notification templates and escalation protocols, and begin with your highest-value agreements where missed obligations would have significant financial impact.
Post-Signature Analytics & Contract Intelligence
One of the most powerful yet underappreciated benefits of Agentic AI is its ability to generate insights into contracting patterns and outcomes. When Sarah’s team received their quarterly analytics report, several surprising findings emerged that changed their approach to negotiations.
The report revealed that the legal team spent 40% of its negotiation time on a specific indemnification clause that counterparties rejected 85% of the time. Contracts reviewed by outside counsel took 3.7 times longer to close with minimal difference in final terms. Three major customers consistently asked for the same changes to data security provisions—suggesting an opportunity to revise the standard template. Perhaps most interestingly, deals closed within 14 days showed 22% higher renewal rates than those with extended negotiations.
Emerging Innovations Shaping the Future of Agentic AI
These insights let Sarah’s team revise templates, adjust approval thresholds, and streamline processes to focus on truly impactful issues rather than fighting battles that historically yielded little benefit.
To implement similar analytics capabilities, define key performance indicators for your contracting process and create a structured data model for capturing negotiation history and outcomes. Establish regular review cycles to analyze contracting trends and implement a feedback loop to continuously refine templates based on actual negotiation results.
Emerging Innovations Shaping the Future of Agentic AI
The capabilities described above represent the current state of Agentic AI in contract management, but the technology continues to advance rapidly. Forward-thinking legal departments are already exploring the next frontier of possibilities.
During a recent merger agreement negotiation, Sarah’s team experimented with an advanced AI agent that served as a virtual negotiation assistant. As counterparty redlines arrived, the system generated real-time counterproposals and gave the negotiation team historical data showing how similar provisions had been resolved in past deals. When the other party proposed ambiguous language in an earn-out provision, the agent forecasted a 73% probability of future dispute based on similar wording in earlier agreements. It suggested three alternative formulations that had historically led to successful outcomes and created an automated negotiation record documenting the evolution of key terms and reasons.
This level of support changed the negotiation process from intuition-based to data-driven, with measurable improvements in outcomes and significant reductions in time-to-signature.
To prepare your organization for these emerging innovations, establish methods for tracking negotiation outcomes and linking them to specific contract provisions. Build institutional knowledge by documenting successful negotiation strategies for different contract types. Create structured feedback systems to help AI systems learn from attorney knowledge and consider pilot programs testing limited AI negotiation assistance on lower-stakes agreements before expanding to more critical transactions.
The Augmented Legal Professional – Maximize Value Using Legal AI
For Sarah and her team, Agentic AI has changed legal contract management from a reactive, document-centric process to a proactive, strategic discipline. Review times that once stretched for days now complete in minutes. Negotiation cycles have gone down by 50%, with more favorable outcomes. Risk identification has improved by 40%, preventing several potential disputes before they materialized. Perhaps most significantly, the team has reallocated 65% of attorney time from routine review to strategic work—elevating the legal department’s role within the organization.
AI Legal Assistant – not Only a Tool but Your Strategic Partner
The lesson from their experience is clear: The greatest value comes not from viewing AI as merely a time-saving tool but as a strategic partner enabling a complete reimagining of legal workflows. The most successful implementations pair AI capabilities with human knowledge —letting attorneys focus on relationship management, complex problem-solving, and business strategy while AI handles routine analysis, documentation, and administration.
If you’re considering implementing Agentic AI in your legal department, start small but think big. Select a single high-volume, lower-risk contract type for your initial pilot. Document baseline metrics before implementation and track improvements in speed, consistency, and quality. Use these early wins to build organizational confidence before expanding to more complex applications.
Conclusion – Embrace Agentic AI to Focus on What Matters
By embracing this approach, legal professionals like Sarah have elevated their practice from document processors to strategic advisors—creating more value for their organizations while engaging in more intellectually rewarding work. Agentic AI doesn’t replace legal knowledge; it amplifies it by handling routine tasks so attorneys can focus on what matters: applying judgment, creativity, and strategic thinking to complex business challenges.
The future of legal contract management isn’t about choosing between human and artificial intelligence—it’s about combining both to create something better than either could achieve alone.
FAQ – AI Legal Assistant & AI Paralegal
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to a new class of intelligent systems capable of initiating and managing actions independently. Unlike traditional AI, which functions primarily in response to explicit instructions, agentic AI systems exhibit autonomy, adapt to evolving conditions, and pursue long-term goals across complex workflows.
This paradigm represents a fundamental shift in artificial intelligence, moving from static automation to dynamic, context-aware decision-making.
What is an Agentic AI-based Legal Assistant?
An AI Legal Assistant is an autonomous software system designed to support legal professionals by executing complex, multi-step tasks across the contract lifecycle with minimal human intervention. Unlike conventional legal technology that relies on manual input or rule-based automation, an AI Legal Assistant—especially when built on Agentic AI principles—understands context, makes decisions, and independently carries out actions such as contract review, drafting, negotiation triage, and obligation tracking.
By proactively identifying issues, suggesting legally compliant alternatives, and coordinating cross-functional approvals, an AI Legal Assistant transforms legal operations from reactive support functions into strategic, data-driven systems.
What are the Key Abilities of an AI Legal Assistant?
Must-have features of a capable Agentic AI Legal Assistant:
- Intelligent contract review and clause comparison,
- Automated drafting using dynamic templates,
- Workflow routing and deadline notifications,
- Obligation tracking and risk profiling,
- Legal analytics for post-signature optimization.
How does Agentic AI handle complex, multi-step problems?
Agentic AI manages complex, multi-step problems by:
- Chaining capabilities such as language understanding, data extraction, risk identification, and task execution,
- Maintaining state awareness across different phases of legal workflows,
- Decomposing high-level objectives into sequential, autonomous tasks,
- Collaborating with external systems like matter management platforms and contract repositories,
- Escalating edge cases to human users with contextual recommendations.
How does Agentic AI handle complex, multi-step workflows?
To manage complex workflows, Agentic AI:
- Autonomously initiates each step without awaiting human prompts
- Monitors contract progress across legal, sales, finance, and compliance stakeholders
- Routes documents based on deviation types and approval logic
- Logs activity and outcomes in internal systems for audit and tracking
- Continuously optimizes based on prior workflow performance and legal outcomes
How does Agentic AI ensure data privacy and security?
Agentic AI maintains data privacy and security by employing encryption, federated learning, enforcing strict access controls, conducting regular system audits to identify vulnerabilities, and utilizing anonymization techniques to safeguard personal information.
What Teams Benefit Most From Agentic AI-based Legal Tools?
- High-volume contract teams (e.g., sales, procurement, compliance)
- Lean in-house legal departments facing resource constraints
- Organizations seeking faster deal velocity and reduced turnaround times
- Legal operations focused on standardization and data capture