T&C Meaning – What are Terms and Conditions, and How to Write Them?
Every contract manager knows this feeling: you’re reviewing your organization’s standard terms and conditions when you realize they haven’t been updated in 5 years, reference discontinued services, and somehow still mention fax numbers as a primary contact method. Meanwhile, your sales team has been sending out three different versions, and nobody’s quite sure which one is current. Sounds familiar?
Terms and conditions represent far more than legal boilerplate at the bottom of a webpage. They serve as the foundation for every business relationship your organization builds, protecting your interests while setting clear expectations for customers and partners.
Whether you’re updating existing agreements, creating new ones, or managing an entire portfolio of contractual relationships, getting your terms and conditions right can mean the difference between smooth operations and costly disputes.
What Are Terms and Conditions – Understanding T&C Meaning
If someone asked you to explain what are terms and conditions to a new team member, you might start with the basics: they’re the rules governing how customers interact with your business. However, the true terms and conditions meaning extends far beyond simple rules of engagement, because these documents create legally enforceable agreements that define rights, responsibilities, and remedies for both parties in a business relationship.
While, according to a study, 91% of users don’t read them, T&C documents function as contracts between service providers and users, establishing the framework within which business transactions occur. They clarify acceptable use policies, payment terms, intellectual property rights, and dispute resolution procedures. Unlike casual agreements, properly drafted terms and conditions create binding obligations that courts can enforce, provided they meet certain legal requirements.
The significance of these agreements varies depending on your business model. A software company might emphasize licensing terms and data security provisions, while a manufacturing firm focuses on delivery schedules and quality standards.
Regardless of industry, these documents serve three critical purposes:
- Protect your business from liability
- Establish operational boundaries
- Create predictable outcomes for both parties
Terms of Agreement vs. Terms and Conditions – Key Distinctions
While many use “terms of agreement” and “terms and conditions” interchangeably, subtle distinctions exist that matter in certain contexts. Terms of agreement typically refers to negotiated contracts where both parties have input into the final document. These agreements often involve back-and-forth discussions, customized provisions, and signatures from both parties.
While terms and conditions usually represent nonnegotiable, standardized agreements that users must accept to access services or make purchases. Think of website T&Cs or app usage policies – users either accept them as written or cannot proceed. This “take it or leave it” nature defines most consumer facing T&Cs.
The distinction becomes important when determining enforceability and managing different agreement types within your organization. Negotiated agreements often carry more weight in disputes because both parties actively participated in creating the terms. Standard T&Cs face greater scrutiny from courts, particularly regarding unusual or onerous provisions that users might not reasonably expect.
Are Terms and Conditions Legally Binding?
Here’s a question that keeps both professionals and users up at night: Are terms and conditions legally binding if nobody actually reads them? The short answer is yes, but with significant caveats that every contract manager should understand.
Courts generally enforce properly constructed T&Cs, but they scrutinize these agreements more carefully than negotiated contracts. The key lies in demonstrating that users had reasonable notice of the terms and manifested acceptance through their actions. Simply burying a link in a website footer won’t suffice if you need to enforce critical provisions later.
Enforceability also depends on the reasonableness of your terms. Courts regularly strike down provisions they deem unconscionable, particularly in consumer contracts. Overly broad limitation of liability clauses, mandatory arbitration in inconvenient venues, or terms that violate consumer protection laws can invalidate portions of your agreement or, worse, the entire document.
Factors That Determine Legal Enforceability

- Conspicuous presentation: Terms must be clearly visible and accessible to users before they complete transactions or begin using services.
- Acceptance method: “Clickwrap” agreements requiring users to actively check a box receive 80% legal enforcement, significantly stronger than “browsewrap” agreements (65%) that assume acceptance through mere website use.
- Language clarity: Courts interpret ambiguous provisions against the drafting party, so using plain language instead of legal jargon strengthens enforceability.
- Legal compliance: Terms must align with applicable laws and cannot override statutory consumer rights or violate public policy.
- Acceptance records: Maintaining documentation of when and how users accepted your terms provides crucial evidence if disputes arise.
- Active vs. passive consent: Requiring explicit actions like checking an “I agree” box creates stronger evidence of acceptance than relying on continued use of services.
Standard Terms and Conditions – Essential Components
Creating comprehensive standard terms and conditions requires balancing legal protection with practical usability. While every business has unique needs, certain provisions appear consistently across effective T&C documents because they address universal concerns in commercial relationships.
A T&C should begin with a clear identification of the parties and the services or products covered. This foundation seems obvious, but ambiguity here can undermine the entire agreement. Following this introduction, payment terms establish when, how, and under what circumstances payment becomes due. For subscription services, this includes renewal terms, price change notifications, and cancellation procedures.
Intellectual property provisions protect your business’s creative assets while clarifying what rights users receive. Limitation of liability clauses – perhaps the most important protective provisions – cap your exposure to damages while remaining reasonable enough to survive judicial review. Termination conditions specify how either party can end the relationship and what happens to data, deliverables, or prepaid fees upon termination.
Privacy and data protection terms have gained prominence as regulations multiply globally. Even if you maintain a separate privacy policy, your T&Cs should reference data handling practices and compliance obligations. Dispute resolution procedures, including governing law and venue selections, determine how conflicts will be resolved, potentially saving significant legal costs through arbitration or mediation requirements.
Business Terms and Conditions – Core Clauses
Every business’s terms and conditions document needs certain fundamental provisions regardless of industry or size. The acceptance clause establishes how users agree to your terms – whether through clicking “I agree,” completing a purchase, or accessing services. Without clear acceptance mechanisms, enforcement becomes nearly impossible.
User obligations define acceptable behavior and usage restrictions. For digital platforms, this includes prohibitions on hacking, data scraping, or posting inappropriate content. Physical product sellers might restrict resale, modification, or commercial use. These provisions protect both your business and other users from harmful activities.
Warranty disclaimers and limitation of liability provisions form your primary legal shields. While consumer protection laws limit how far these can go, properly drafted disclaimers significantly reduce exposure to claims. Indemnification clauses require users to defend you against claims arising from their misuse of your services or violation of your terms.
Modification provisions preserve your right to update terms as business needs evolve. Include notice requirements and specify whether continued use constitutes acceptance of changes. Contact information and governing law round out the core provisions every business needs.
Purchase Order Terms and Conditions – Special Considerations
Purchase order terms and conditions require additional provisions that address the unique aspects of procurement relationships. Delivery terms specify not just when products arrive, but also risk transfer points, inspection rights, and rejection procedures. These details prevent disputes over damaged goods or nonconforming deliveries.
Payment terms in purchase orders often include more complexity than standard consumer T&Cs. Net payment periods, early payment discounts, and late payment penalties require precise definition. Specify what constitutes acceptable delivery documentation and when payment obligations trigger.
Quality standards and acceptance criteria deserve special attention in purchase order agreements. Define measurable standards, testing procedures, and remediation requirements for nonconforming goods. Include provisions for partial deliveries, backorders, and allocation during shortages. Warranty terms should address both express and implied warranties, specifying duration, coverage, and claim procedures.
How to Write Terms and Conditions
You’ve probably encountered terms and conditions that read like they were written decades ago – dense paragraphs of legalese that would challenge even experienced attorneys to decipher. If your users can’t understand your terms, courts might not enforce them. Learning how to write terms and conditions effectively means balancing legal protection with practical clarity.
Start with a clear understanding of your business model and risk profile.
- What are your biggest liability exposures?
- Which customer behaviors could damage your business?
- What regulatory requirements apply to your industry?
These questions shape your drafting priorities. A data analytics firm needs robust data security and confidentiality provisions, while a dropshipping business might prioritize shipping disclaimers and return policies.
Structure your document logically, using headers and numbered sections for easy reference. Begin with definitions if you’ll use specific terms repeatedly. Place your most important provisions, typically acceptance, payment, and liability limitations, early in the document. Use short sentences and paragraphs. When complex legal concepts require inclusion, follow them with plain language summaries or examples.
Consider your enforcement needs carefully. Overly aggressive terms might deter customers or invite regulatory scrutiny. Conversely, overly permissive terms leave you vulnerable to abuse. The goal is to create terms that protect your legitimate interests while remaining fair enough to maintain customer relationships and survive legal challenges. Regular reviews ensure your terms evolve with your business and changing legal requirements.
Using a Terms and Conditions Template – Benefits and Limitations
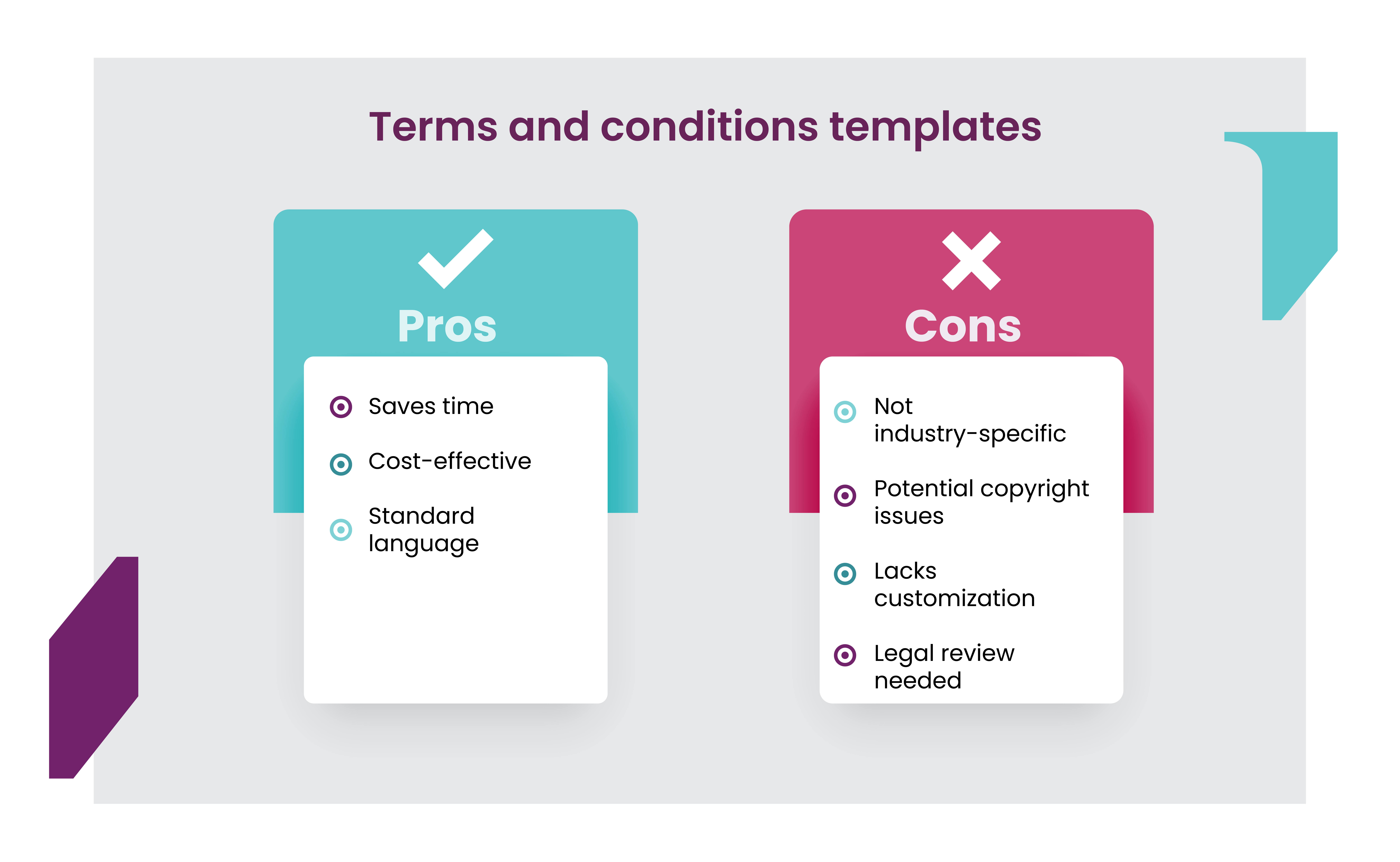
A terms and conditions template can jumpstart your drafting process, providing structure and reminding you of provisions you might otherwise overlook. Quality templates include standard legal language tested across many businesses, potentially saving legal fees for smaller organizations or those just starting.
However, templates have significant limitations that many businesses discover only when trying to enforce their terms. Generic provisions might not address your specific business model, leaving gaps in protection. Industry specific regulations often require customized terms that templates cannot anticipate. More concerning, using unchanged templates from other businesses might constitute copyright infringement.
The most effective approach combines template structure with customized content. Use templates to ensure you haven’t missed essential provisions, but adapt each section to reflect your actual business practices. Consider templates as starting points rather than finished products. Have legal counsel review your customized version, particularly if you operate in regulated industries or face significant liability exposure.
Industry Specific T&C Requirements
Different industries face vastly different regulatory requirements, operational risks, and customer expectations that shape their contractual needs. What works for a software company could leave a medical device manufacturer exposed to regulatory penalties or product liability claims.
Life Sciences T&C Considerations
Life sciences companies operate under intense regulatory scrutiny that shapes every aspect of their terms and conditions. FDA compliance requirements, clinical trial protocols, and adverse event reporting obligations must be clearly addressed. Terms often include detailed provisions about regulatory approvals, product recalls, and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Intellectual property provisions take on heightened importance given the massive investments in research and development. Patent rights, trade secrets, and proprietary formulations require robust protection. Collaboration agreements must carefully delineate ownership of improvements, joint inventions, and background intellectual property.
Product liability and indemnification receive extensive treatment, given the potential for serious adverse events. Terms must address clinical trial insurance, product liability coverage, and procedures for handling adverse event reports while maintaining compliance with pharmacovigilance requirements.
Retail and CPG Terms and Conditions
Retail and consumer packaged goods businesses face unique challenges in balancing consumer protection requirements with operational efficiency. Return policies must comply with varying state and national consumer rights laws while remaining economically viable. Terms must address everything from defective products to buyer’s remorse returns.
Warranty provisions require careful drafting to avoid creating obligations beyond those intended. Express warranties, implied warranties of merchantability, and fitness for a particular purpose all need consideration. Many CPG companies include detailed limitation periods and claim procedures to manage warranty exposure.
Supply chain complexity adds another layer of consideration. Terms often need to address dropshipping arrangements, third party fulfillment, and marketplace selling. Product safety standards, recall procedures, and crisis management protocols deserve inclusion, particularly for products that could pose safety risks.
Terms and Conditions for Ecommerce
Digital commerce brings unique challenges that terms and conditions for ecommerce must address. Online transactions lack the face-to-face interactions that build trust in traditional retail, making clear terms even more critical for setting expectations and preventing disputes.
Product descriptions and accuracy disclaimers protect against claims when items don’t match customer expectations. Include provisions addressing color variations on different screens, sizing discrepancies, and the possibility of errors in product listings. Digital delivery terms specify how and when digital products become available, license restrictions, and technical requirements.
International sales complicate ecommerce terms significantly. Address currency conversions, customs duties, import restrictions, and varying consumer protection laws. Specify which countries you ship to and any restrictions on product availability. Include provisions for handling returns from international customers, who may face different legal requirements than domestic buyers.
Payment processing terms should cover accepted payment methods, currency, timing of charges, and procedures for failed transactions. Address what happens with preorders, backorders, and situations where pricing errors occur. Security provisions assuring customers about payment data protection have become essential for building trust.
Beyond drafting comprehensive terms, ecommerce businesses face the practical challenge of implementation – ensuring terms are properly presented and accepted before transactions complete. This is where the automated clickwrap solution, Malbek Klix, transforms a manual, error-prone process into a seamless operation.
Instead of relying on developers to update terms across multiple pages whenever legal makes changes, Klix enables legal teams to push updates directly through an embedded widget. The terms automatically update everywhere they appear, maintaining consistent enforcement while eliminating the delays and version control issues that plague manual updates. For high-volume ecommerce operations, this automation ensures every transaction has properly accepted, legally enforceable terms without slowing down the customer experience.
Manufacturing Sector T&C Essentials
Manufacturing agreements demand precise specifications around quality standards, tolerances, and acceptance criteria. Terms must establish clear inspection rights, testing procedures, and remedies for nonconforming goods. Defining what constitutes acceptable quality levels and how defects will be measured prevents disputes.
Delivery and logistics terms take on critical importance when production schedules and just in time inventory systems depend on reliable supply. Force majeure provisions, allocation during shortages, and penalties for late delivery require a careful balance between protecting both parties’ interests.
Tooling, equipment, and intellectual property ownership need explicit treatment. Who owns custom molds, dies, or specifications? How will improvements or modifications be handled? These questions become crucial when relationships end or when considering alternative suppliers.
Managing T&Cs at Scale with Contract Lifecycle Management
Think about the last time your legal team needed to update standard terms across all business units. How long did it take to locate every version, ensure consistency, and confirm implementation? For organizations managing hundreds or thousands of agreements, manual T&C management becomes not just inefficient and risky.
Instead of scattered Word documents and email chains, Contract Lifecycle Management platforms centralize terms management, ensuring everyone uses current versions. Automated workflows route proposed changes through appropriate approvals, maintaining compliance while accelerating updates.
Advanced CLM capabilities like those offered in Malbek’s platform go beyond simple document storage. AI powered analysis can identify nonstandard terms across your agreement portfolio, flagging deviations that might create unexpected risks. Smart tagging and clause libraries ensure consistency while allowing necessary customization. Integration with upstream and downstream systems means your terms flow seamlessly through your entire contracting process.
The real value emerges when dealing with regulatory changes or business model evolution. When GDPR required privacy term updates, organizations using CLM solutions could identify affected agreements, deploy updated language, and track acceptance across their entire customer base. This capability transforms terms management from a reactive scramble into a strategic advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions – Terms and Conditions
What’s the difference between standard terms and conditions and customized agreements?
Standard terms and conditions are nonnegotiable agreements that apply uniformly to all users or customers, typically presented on a “take it or leave it” basis. Customized agreements involve negotiation between parties, with tailored provisions reflecting specific deal terms or relationship requirements. While standard terms offer efficiency and consistency, customized agreements provide flexibility for complex or high value transactions.
How often should businesses update their terms and conditions template?
Review your terms and conditions template at least annually, but trigger immediate reviews when major changes occur – new regulations, business model shifts, significant disputes, or expansion into new markets. Regular audits help identify outdated provisions, ensure regulatory compliance, and adapt to evolving business needs. Document version histories and user acceptance to maintain enforceability.
What makes purchase order terms and conditions different from general business terms?
Purchase order terms and conditions focus specifically on procurement transactions, emphasizing delivery schedules, quality standards, inspection rights, and payment terms tied to goods receipt. General business terms cover broader relationship aspects like service delivery, intellectual property, and ongoing obligations. Purchase order terms typically include more detailed provisions about risk transfer, warranties, and remedies for nonconforming goods.
Can terms and conditions examples from other companies be legally copied?
Copying another company’s terms and conditions can violate copyright law and create serious legal risks. Beyond potential infringement claims, copied terms likely won’t match your business model, potentially leaving gaps in protection or creating obligations you didn’t intend. Instead, use industry resources and templates as inspiration while drafting original terms that reflect your specific business needs.
Wrap Up
Whether you’re updating existing agreements, evaluating standard terms and conditions, or implementing enterprise wide contract management solutions, remember that effective T&Cs balance protection with practicality. The goal isn’t creating impenetrable legal fortresses but establishing clear, enforceable agreements that support business objectives while managing risk appropriately.
Ready to see how Malbek can transform your contract management? Schedule a personalized demo to discover how AI powered CLM can reduce contract review time, minimize compliance risks, and give your team the tools they need to manage terms and conditions at scale. Contact our team to learn more about bringing intelligence to your contract lifecycle.