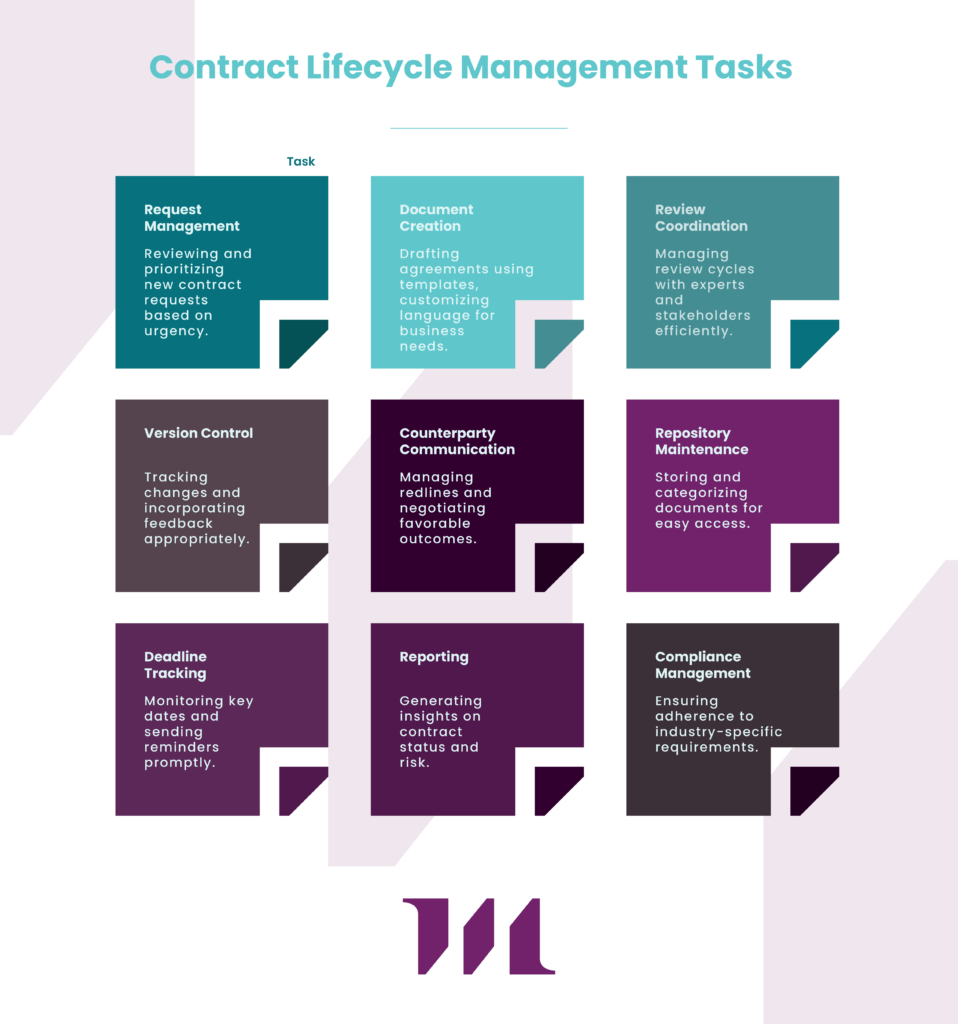
What keeps experienced lawyers and contract managers awake at night? Often, it’s the thought of their organization paying for someone else’s mistakes. Without a thoughtfully drafted indemnification clause, this nightmare can become a reality. These provisions serve as critical risk management tools, defining who bears financial responsibility when business relationships go sideways. An indemnification clause acts as your contract’s built-in insurance policy, establishing clear rules for risk allocation before problems arise.
This article explores the mechanics of indemnification clauses, with special focus on mutual indemnification arrangements that create balanced risk-sharing between parties. Whether you’re reviewing existing contracts or negotiating new agreements, you’ll discover practical strategies for managing indemnification provisions that protect your interests without derailing deals.
What Is an Indemnification Clause?
Ever wondered why lawyers spend so much time debating a single paragraph in a 50-page contract? When that paragraph is an indemnification clause, there’s good reason for the scrutiny. These provisions can mean the difference between a minor inconvenience and a major financial disaster when disputes arise.
An indemnification clause is a contractual provision where one party (the indemnifier) agrees to compensate another party (the indemnitee) for specific losses, damages, or liabilities that may occur during their business relationship. Think of it as a pre-agreed insurance arrangement built directly into your contract. The indemnifying party essentially promises to cover certain costs if particular events happen, shifting financial risk away from the indemnified party.
This clause addresses a fundamental business question: Who should bear the cost when something goes wrong? The answer varies based on industry standards, transaction types, and negotiating leverage. A software licensing agreement might focus on intellectual property infringement claims, while a construction contract likely would emphasize personal injury and property damage.
Parties can customize these clauses to address specific concerns, set monetary limits, and define precise triggering events. This customization allows businesses to enter agreements with greater confidence, knowing their potential exposure is clearly defined and manageable.
The Role of the Indemnifying Party and Indemnified Party
There are distinct purposes for having an indemnification clause:

There are also specific obligations for the indemnifying and indemnified parties as follows.
Indemnifying Party Obligations:
- Bears the obligation to protect and compensate the other party
- Acts as a financial backstop when covered events occur
- Pays for losses, legal fees, and costs as stipulated within the scope section of the indemnification clause
- Often controls the defense of (and choice of counsel tasked with defending) third-party claims
- Must maintain adequate financial resources, including insurance coverage to fulfill obligations
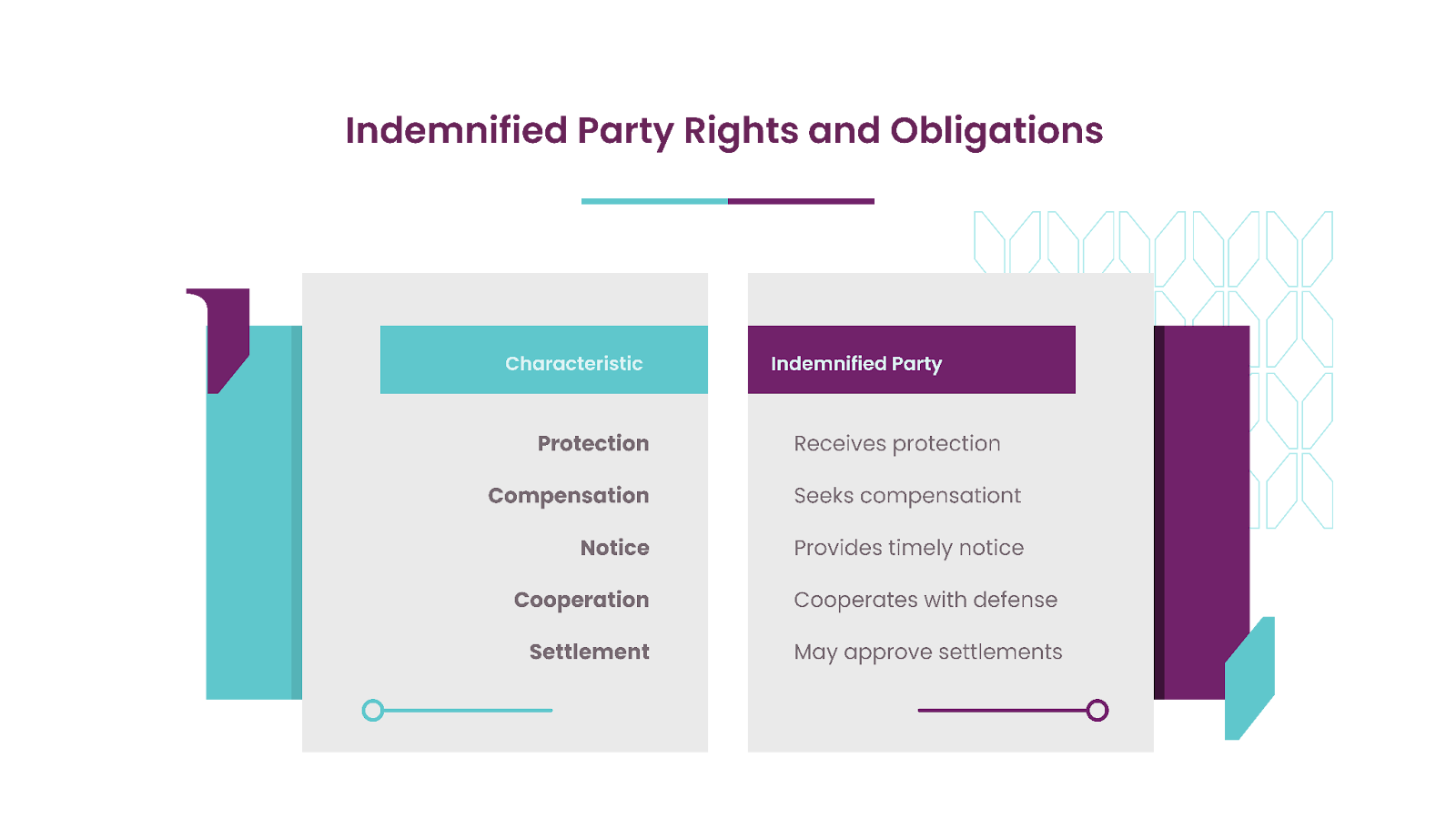
Indemnified Party rights:
- Receives protection under the agreement
- Can seek compensation rather than bearing costs directly
- Must provide timely notice of claims
- Usually required to cooperate with defense efforts
- May have approval rights over settlements
These roles often overlap in commercial relationships, with parties alternating between indemnifier and indemnitee for different risk types, creating reciprocal protection arrangements.
How Does an Indemnification Clause in a Contract Work?
The mechanics of indemnification follow a logical sequence. When a triggering event occurs, such as a breach of warranty, negligence, or a third-party claim, the indemnification process activates. The indemnified party must notify the indemnifier promptly, providing details about the loss or claim.
Once notified, the indemnifying party typically gains control over defending third-party claims. This includes selecting attorneys, making strategic decisions, and negotiating settlements. The indemnified party must cooperate, providing information and assistance as needed.
Payment obligations vary by agreement structure. Some contracts require the indemnifier to pay costs immediately, while others allow reimbursement after the indemnified party has paid. The specific language of the indemnification clause in the contract determines these procedural details, making precise drafting essential.
Understanding Mutual Indemnification
Mutual indemnification creates a balanced ecosystem where each party protects the other from their respective mistakes. Unlike one sided arrangements, this approach acknowledges that both parties contribute to potential risks.
A mutual indemnification clause represents an agreement where both parties serve as indemnifier and indemnitee, depending on the circumstances. Each party compensates the other for losses arising from their own actions, negligence, or breaches. This reciprocal arrangement inherently promotes fairness and accountability.
The beauty of mutual indemnification lies in preventing either party from shifting all risk to the other. When a software company and client agree to mutual indemnification, the company covers losses from code defects while the client covers losses from data inaccuracies. Each party remains accountable for the risks they control.
This balanced approach suits relationships where both parties actively participate in value creation. Joint ventures, strategic partnerships, and complex service arrangements benefit from mutual indemnification because both parties contribute expertise and decision making that could lead to liability.
Mutual Indemnification vs. One-Sided Indemnification
The choice between mutual and one-sided indemnification reflects business dynamics and bargaining power. One-sided indemnification places all obligations on a single party, typically seen in relationships with clear risk disparities or negotiating leverage differences. Large corporations often demand one-sided or broad indemnification from smaller vendors on the basis that a vendor is best positioned to bear the majority of product or service risks.
Recent contract data reveals the reality of indemnification negotiations in practice. A study of negotiated vendor agreements shows that 72% include customer indemnification obligations, demonstrating vendors’ success in securing reciprocal protection. However, the specific claims covered tell a more nuanced story—third-party IP infringement (52%) and customers’ content, data, and materials (42%) top the list of indemnified claims. This distribution suggests effective negotiation where both parties achieve meaningful wins: vendors secure indemnification coverage while customers limit that coverage to risks within their control.
Mutual indemnification offers advantages: it promotes partnership over subordination, simplifies negotiations, and encourages high standards from both parties. Courts generally view mutual provisions more favorably than one-sided arrangements, particularly regarding unconscionability claims. The reciprocal nature makes agreements more sustainable and fair.
Key Components of a Mutual Indemnification Clause
Essential elements for effective mutual indemnification:
Triggering Events:
- Breaches of contract terms
- Negligent acts or omissions
- Willful misconduct
- Violations of applicable laws
- Intellectual property infringement
- Confidentiality breaches
Covered Losses:
- Direct damages
- Third-party claims
- Legal fees and costs
- Settlement amounts
- Investigation expenses
- Court judgments
Common Exclusions:
- Consequential or indirect damages
- Lost profits
- Punitive damages
- Sole negligence of the indemnified party
- Assumed contractual liabilities
Procedural Requirements:
- Notice deadlines (typically 10-30 days)
- Cooperation obligations
- Defense control provisions
- Settlement approval rights
- Insurance coordination
- Survival periods post-termination
You can read more about the essential considerations when creating indemnification clauses here.
Benefits and Applications of Indemnification Clauses
Why do seasoned lawyers and contract professionals treat indemnification clauses so carefully? These provisions address multiple challenges simultaneously, from protecting against unforeseen liabilities to clarifying responsibilities before disputes arise.
The primary benefit lies in efficient risk allocation. Rather than leaving liability questions to chance or litigation, indemnification provisions establish clear rules upfront. This certainty allows businesses to price services appropriately, obtain suitable insurance, and make informed decisions about contract risks.
Indemnification serves as a powerful negotiation tool. When one party demands extensive warranties, the other can propose indemnification provisions limiting exposure to reasonable levels. This give-and-take creates sustainable agreements where both parties feel protected. Beyond risk allocation, these clauses also encourage reasonable risk management.
Common Business Scenarios Requiring Indemnification
Technology agreements frequently require comprehensive indemnification. Software developers indemnify clients against intellectual property claims, while clients indemnify developers for data breaches from inadequate security. These reciprocal protections reflect shared responsibilities in technology solutions.
Service agreements across industries rely on indemnification for liability management. Marketing agencies indemnify clients for copyright violations, while clients indemnify agencies for providing inaccurate information. Professional service providers use indemnification to limit exposure while standing behind their work product.
Manufacturing and distribution relationships present unique challenges. Product liability drives manufacturers to seek indemnification from distributors for improper handling, while distributors want protection from defects. Construction contracts layer multiple obligations among owners, contractors, and subcontractors, creating complex protection webs.
Risk Management Through Strategic Indemnification
Strategic indemnification converts contract portfolios from liability risks into controlled exposures. Effective managers analyze organizational risk to develop standard positions that balance protection with commercial viability, ensuring consistent exposure across all agreements.
Insurance integration amplifies protection. Requiring indemnifiers to maintain specific coverage and additional insured status creates a layered defense—insurance handles primary exposure while contractual indemnification covers exclusions and excess amounts.
Regular portfolio reviews expose risk concentrations and gaps. Organizations often find they’ve granted broad indemnification to customers without securing equivalent vendor protection. Identifying these imbalances enables targeted corrections through contract amendments or revised negotiation strategies.
Market dynamics also influence indemnification strategies, as evidenced by trends in specialized transactions. In M&A deals, for example, ABA studies from 2005-2021 show indemnity caps declining consistently as a percentage of transaction value. The 2008 financial crisis temporarily reversed this trend when buyer-friendly markets pushed caps higher, demonstrating how economic conditions shape indemnification negotiations.
While M&A transactions differ from typical commercial contracts, this trend illustrates a broader principle: organizations must adapt their indemnification strategies to reflect current market conditions and bargaining dynamics.
Managing Indemnification Clauses with Modern CLM Technology
Remember scrolling through hundreds of contracts searching for that one indemnification provision you vaguely recall negotiating? Contract lifecycle management technology transforms this needle-in-a-haystack exercise into simple database queries, taking seconds instead of hours. Leading platforms like Malbek demonstrate how efficiency gains extend beyond time savings—CLM systems provide insights into risk exposure that manual review could never achieve.
CLM platforms excel at capturing and categorizing indemnification provisions across entire portfolios. Advanced systems like Malbek identify whether contracts contain these clauses, classify them as mutual or one-sided, and extract key terms like liability caps, exclusions, or survival periods. This visibility reveals aggregate exposure and identifies contracts needing renegotiation when business circumstances change. Real-time dashboards show total indemnification exposure by counterparty, geography, or business unit, giving organizations the comprehensive view they need for strategic risk management.
Real power emerges when systems track obligations throughout the contract lifecycle. Malbek’s automated alerts remind teams of notice deadlines for potential claims, ensuring procedural requirements don’t void indemnification rights. Insurance integration ensures coverage adequacy for indemnification obligations, flagging gaps before they become problems. When claims arise, the platform provides instant access to relevant terms, prior correspondence, and related documentation, accelerating response times and improving outcomes.
Analytics transform raw data into actionable insights for strategic decision-making. Organizations using Malbek can identify which agreement types generate the most claims, which counterparties frequently trigger obligations, and whether standard language effectively protects interests. Predictive models can even forecast likely claim areas based on historical patterns. These insights drive continuous improvement in templates and negotiation strategies while informing business decisions about risk acceptance.
Automation and AI in Indemnification Management
Artificial intelligence brings powerful capabilities to indemnification management that transform how organizations handle these critical provisions. Malbek’s AI-powered analysis reviews incoming contracts at scale, flagging unusual provisions deviating from company standards or market norms. This automated review catches issues human reviewers might miss in high-volume environments while ensuring consistency across the organization.
Natural language processing enables systems to understand provisions despite drafting variations. Whether contracts use “indemnify and hold harmless” or “defend and reimburse,” Malbek’s AI recognizes functional equivalence and extracts key terms accurately. This semantic understanding improves search accuracy and enables comprehensive tracking regardless of specific wording choices. Machine learning continuously improves recognition accuracy as it processes more contracts, making the system smarter over time.
Predictive analytics moves beyond reactive tracking to proactive management of indemnification risks. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical claims data to predict which contracts are likely to generate future indemnification claims. This insight allows better resource allocation, such as requiring additional insurance for high-risk agreements or implementing stricter performance monitoring. Malbek’s risk scoring models can even suggest optimal indemnification terms based on counterparty characteristics and transaction types, helping organizations negotiate from positions of knowledge rather than guesswork.
Best Practices for Ongoing Indemnification Monitoring
Effective indemnification management demands vigilant oversight throughout the entire contract lifecycle. Smart organizations develop comprehensive monitoring systems that operate on multiple levels, starting with regular portfolio reviews. These quarterly assessments help identify shifting risk patterns before they become problematic, while annual insurance reviews ensure that coverage keeps pace with evolving indemnification obligations. The key is creating a rhythm of review that catches issues early, whether through monthly trigger event monitoring or deep-dive analyses of claims history that reveal which types of agreements generate the most exposure.
Behind every successful monitoring program lies a framework of standardized procedures that transform reactive scrambling into proactive management. When potential claims arise, having clear notification protocols with defined escalation timelines, typically 24 to 48 hours, ensures nothing falls through the cracks. These procedures extend beyond simple alerts to encompass document preservation strategies, response guidelines tailored to different claim stages, and predetermined settlement authorities that prevent costly delays. The most effective organizations recognize that indemnification management crosses departmental boundaries, requiring seamless coordination between legal, risk management, and business teams, with established criteria for when external counsel involvement becomes necessary.
Technology serves as the backbone that makes comprehensive monitoring feasible at scale. Modern platforms automate the countless deadlines and checkpoints that human memory alone cannot reliably track, from insurance renewal dates to claim notification windows. These systems integrate claims management workflows with risk scoring algorithms that evolve based on actual experience, providing executives with real-time dashboards that translate complex indemnification data into actionable insights. This technological foundation extends to vendor relationships, where continuous monitoring of financial stability, insurance compliance, and claims history creates early warning systems for potential issues. By aligning vendor management with indemnification oversight and coordinating with procurement during renewal cycles, organizations transform what could be scattered, reactive processes into a unified risk management strategy.
What is an indemnification clause without proper management? Often, an invitation to disputes and unexpected costs that could have been avoided with systematic oversight.
Frequently Asked Questions – Indemnification Clauses
What is the difference between indemnification and a hold harmless clause?
While often used together, indemnification and hold harmless provisions serve slightly different purposes. Indemnification typically involves one party reimbursing another for losses incurred. Hold harmless clauses prevent one party from bringing claims against the other. Many contracts combine both concepts using “indemnify and hold harmless” language. Some jurisdictions treat them synonymously, while others recognize distinct effects.
Can an indemnification clause be enforced if it’s too broad?
Courts scrutinize overly broad clauses and may refuse enforcement, especially if they appear unconscionable. Provisions indemnifying parties for gross negligence or intentional misconduct face challenges. Similarly, unclear, unlimited, or disproportionate obligations may be unenforceable. Clear, specific language limiting indemnification to reasonable scenarios improves enforceability.
How do limitation of liability clauses interact with indemnification provisions?
The relationship requires careful coordination. Some contracts state that indemnification obligations are subject to liability caps, while others carve out indemnification from limitations. Without clear language, disputes arise about whether caps apply. Best practice explicitly states whether and how limitations affect indemnification obligations.
What types of damages are typically excluded from indemnification?
Common exclusions include consequential damages, lost profits, punitive damages, and losses from the indemnified party’s sole negligence. Many provisions exclude damages that could have been mitigated or result from explicitly assumed risks. These exclusions keep obligations commercially reasonable and insurable.
How should insurance requirements be addressed in mutual indemnification clauses?
Requirements should specify minimum coverage amounts, policy types, and additional insured designations. Clauses should clarify whether insurance provides primary coverage or contractual indemnification applies regardless. Including proof requirements and change notifications ensures adequate protection throughout the term.
Conclusion
Mastering indemnification clauses, especially mutual indemnification arrangements, represents a critical skill for contract professionals protecting organizations while maintaining fair relationships. These provisions do more than allocate risk; they create accountability frameworks encouraging responsible behavior and providing clarity when disputes arise.
Success lies in balance. Whether reviewing an indemnity clause or negotiating new terms, focus on provisions fairly distributing risk based on each party’s control and capabilities. Clear language, reasonable scope, and proper integration with insurance transform indemnification from conflict sources into sustainable relationship tools.
As portfolios grow complex, leveraging technology to track obligations becomes essential. CLM platforms provide visibility and control needed to monitor exposure, ensure compliance, and make informed risk decisions. Combined with thoughtful drafting and regular review, these tools enable confident indemnification handling, turning potential liabilities into manageable risks, supporting growth.
If you are interested in knowing more about what Malbek can bring to the table, how it can streamline your processes, ease administrative work, and make contract lifecycle management faster and safer, get in touch with our customer success team today.